Download this example as Julia file or Jupyter notebook.
SW07 - k=0 kagome antiferromagnet
This is a Sunny port of SpinW Tutorial 7, originally authored by Bjorn Fak and Sandor Toth. It calculates the spin wave spectrum of the kagome lattice with antiferromagnetic interactions, with ordering wavevector of $𝐤 = 0$, and relative rotation 120° between sublattices
Load Sunny and the GLMakie plotting package.
using Sunny, GLMakieDefine the chemical cell of a kagome lattice with spacegroup 147 (P-3).
units = Units(:meV, :angstrom)
latvecs = lattice_vectors(6, 6, 8, 90, 90, 120)
cryst = Crystal(latvecs, [[1/2, 0, 0]], 147)
view_crystal(cryst; ndims=2)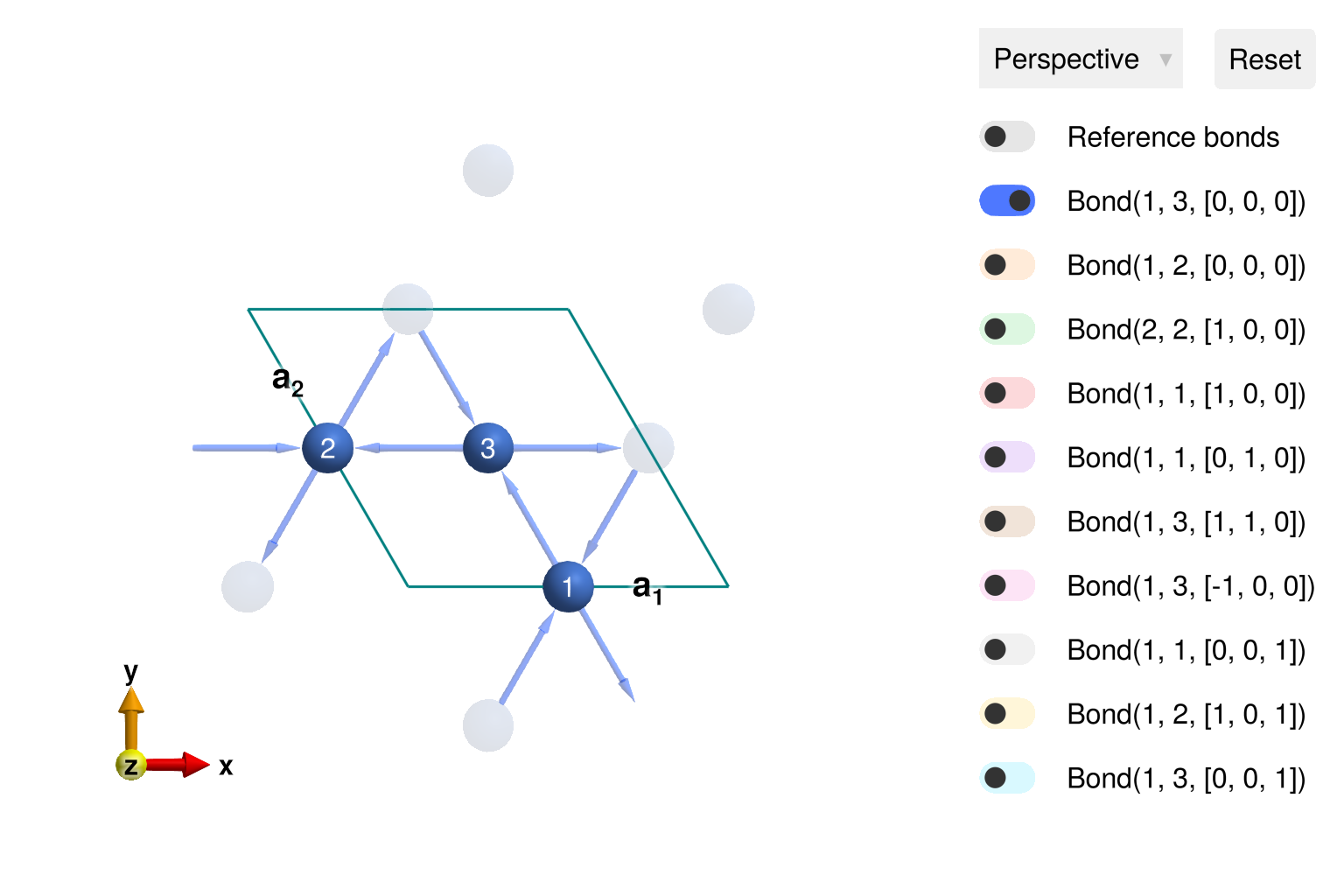
Construct a spin system with nearest and next-nearest neighbor antiferromagnetic interactions. Energy minimization determines a $𝐤 = 0$ magnetic order with 120° rotation between the three sublattices. The overall global rotation in spin-space is arbitrary.
sys = System(cryst, [1 => Moment(s=1, g=2)], :dipole)
J1 = 1.0
J2 = 0.11
set_exchange!(sys, J1, Bond(2, 3, [0, 0, 0]))
set_exchange!(sys, J2, Bond(2, 1, [0, 0, 0]))
randomize_spins!(sys)
minimize_energy!(sys)
plot_spins(sys; ndims=2)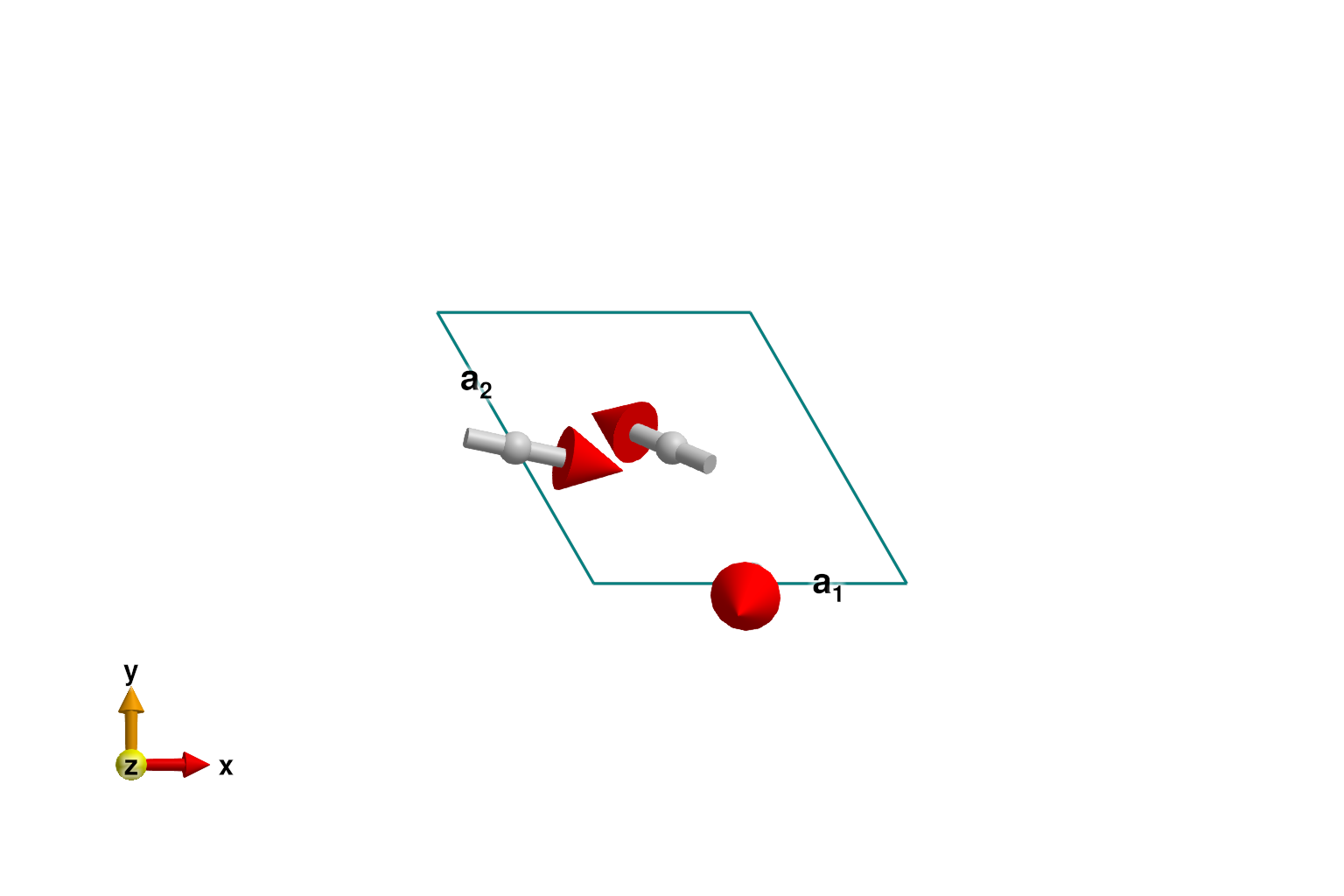
Calculate and plot intensities for a path through $𝐪$-space.
swt = SpinWaveTheory(sys; measure=ssf_perp(sys))
qs = [[-1/2,0,0], [0,0,0], [1/2,1/2,0]]
path = q_space_path(cryst, qs, 400)
res = intensities_bands(swt, path)
plot_intensities(res; units)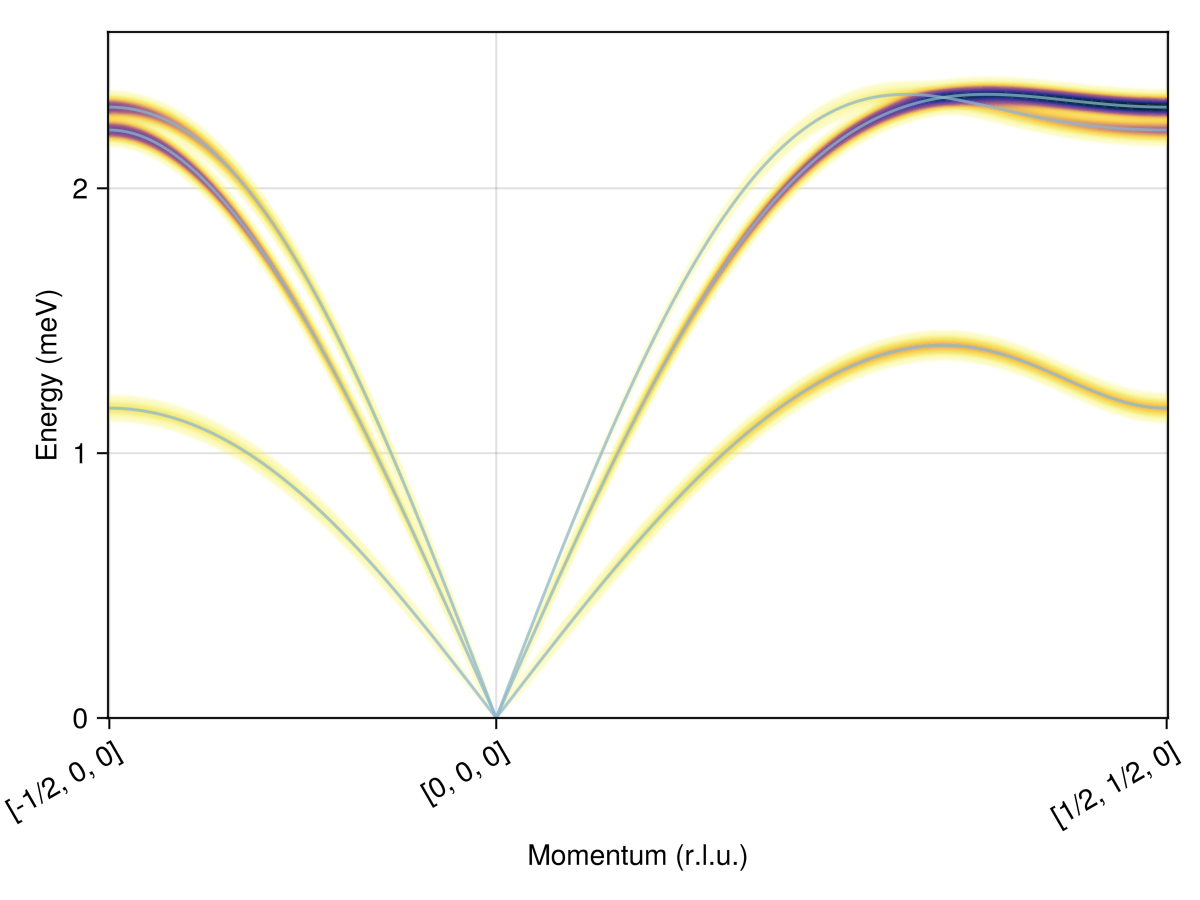
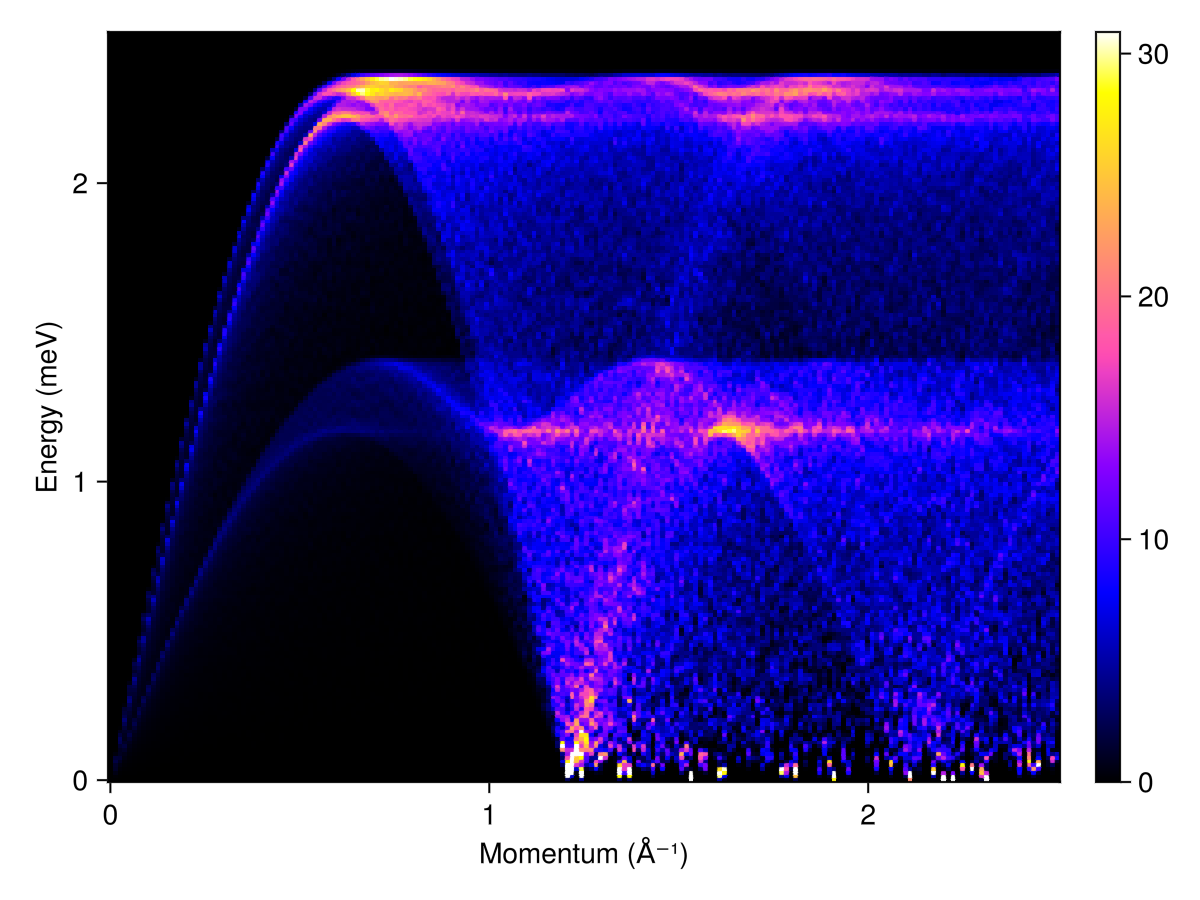
Calculate and plot the powder averaged spectrum
radii = range(0, 2.5, 200)
energies = range(0, 2.5, 200)
kernel = gaussian(fwhm=0.02)
res = powder_average(cryst, radii, 1000) do qs
intensities(swt, qs; energies, kernel)
end
plot_intensities(res; units)